RB signalingCell Death and Biology Diagrams While the identity of P16γ or P12 as a tumor suppressor remains to be established, it is safe to state that P16, P15, and P14ARF together constitute one of the primary anti-tumor defenses in human through strict regulation of both pRb and P53 pathways. Currently, p16 Ink4a is considered a tumor suppressor protein because of its physiological role and downregulated expression in a large number of tumors. While the molecular mechanism of senescence involves p16 and p53 tumor suppressor genes and telomere shortening, this review is focused on the mechanism of p16 control. The p16 mediated senescence acts through the retinoblastoma (Rb) pathway inhibiting the action of the cyclin dependant kinases leading to G1 cell cycle arrest.
Another consequence of the E7-mediated pRb degradation is the overexpression of p16, a potent tumor suppressor. The detection of p16 overexpression has been adopted as a molecular hallmark of HPV-associated OPSCCs, with studies demonstrating its positive effect on patient survival.

Restoration of the Tumor Suppressor Function of Y220C Biology Diagrams
Abstract. p16INK4A and p53 are two major tumor suppressor proteins that are both upregulated in response to various cellular stresses and during senescence and aging. p53 is a well-characterized transcription factor, while p16INK4A a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor encoded by the CDKN2A gene, and controls the expression of several genes through protein-protein interactions and also via
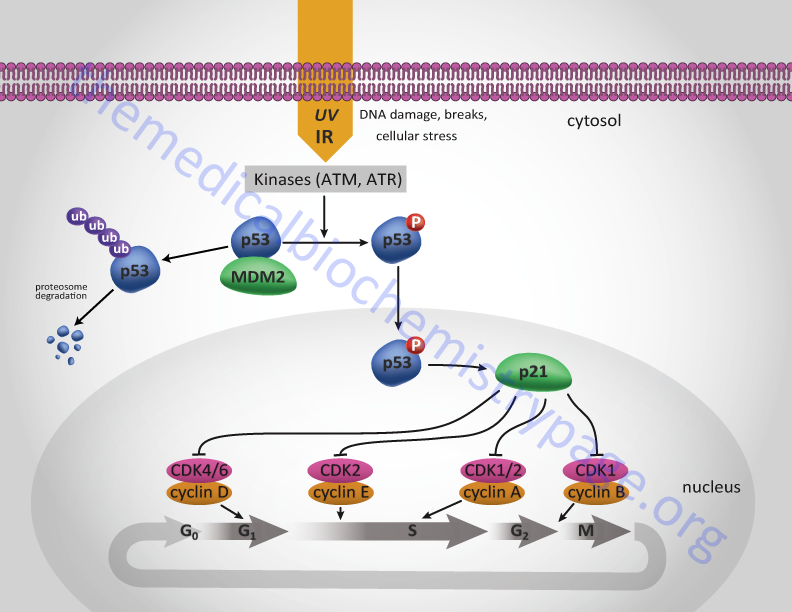
Here, we describe rezatapopt (PC14586), part of a series of compounds designed to reactivate the p53 Y220C mutant. These compounds restore p53 tumor suppressor function by correcting its conformation and enabling it to bind DNA and activate downstream target genes, thus inducing anti-proliferative changes in tumor cells. Additionally, the loss of p16 may be an early event in cancer progression, because deletion of at least one copy is quite high in some premalignant lesions. p16 is a major target in carcinogenesis, rivaled in frequency only by the p53 tumor-suppressor gene. Here, we provide an overview of the important roles of p53, p21, and p16 in the cell-intrinsic checkpoint, signaling, and repair responses to prevent genome instability. The significance of these tumor suppressors is also discussed in the context of cancer and DNA-damaging therapies designed to specifically target tumor cells.
