SOLUTION Anatomy of the shoulder joint Biology Diagrams Learn about the shoulder joint complex, which consists of four articulations: glenohumeral, acromioclavicular, sternoclavicular and scapulothoracic. Find out the articular surfaces, ligaments, bursae, relations, arteries, nerves and movements of the shoulder joint. Learn about the two joints that connect your shoulder blade, upper arm and collarbone. Find out how they work, what conditions can affect them and how to keep them healthy.

Learn about the bones, muscles, ligaments, and movements of the shoulder joint, one of the most complex and mobile joints of the body. Find out how the shoulder joint can be affected by injuries, diseases, and conditions such as rotator cuff tear, frozen shoulder, and labral tear.

Structure, Location, Function, Diagram, Anatomy Biology Diagrams
Learn about the shoulder joint, a synovial ball-and-socket joint that allows for a wide range of motion but is unstable. Find out the articular surfaces, ligaments, capsule, innervation, blood supply and muscles of the glenohumeral joint. Learn about the shoulder joint, a ball-and-socket joint that allows for a wide range of movements. Find out the bones, ligaments, muscles, nerves, and blood vessels that make up the shoulder joint and its clinical significance.
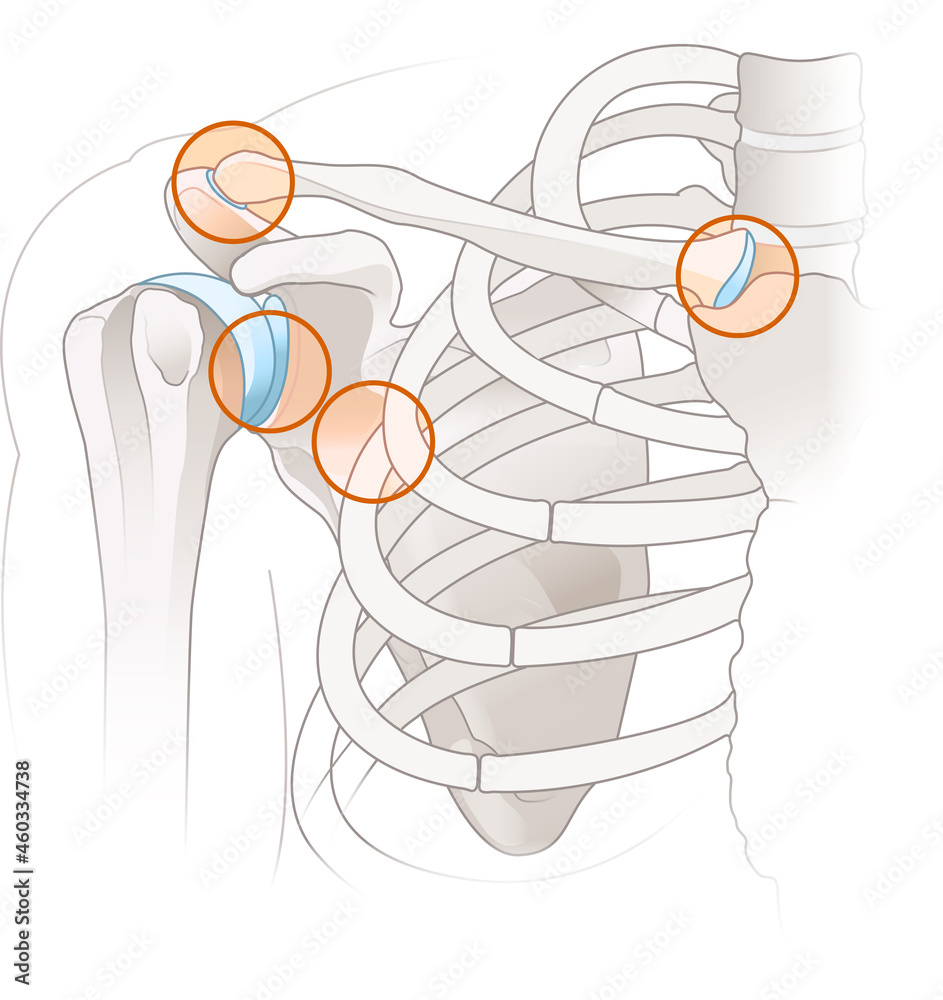
Learn about the two joints that form the shoulder, the glenohumeral and acromioclavicular joints, and how they enable the arm to move in various directions. See 3D images and diagrams of the shoulder bones, muscles, ligaments, and cartilage. Learn about the anatomy of the shoulder joint, a ball and socket synovial joint that allows a wide range of movement. Find out how the joint is stabilised by ligaments, muscles, bursae and the glenoid labrum, and what are the common injuries and clinical relevance of the shoulder joint. Learn about the two joints and the rotator cuff that make up the shoulder, and how they can be injured. The web page also explains the anatomy of the acromioclavicular joint and the glenohumeral joint, and the role of the labrum and the joint capsule.
