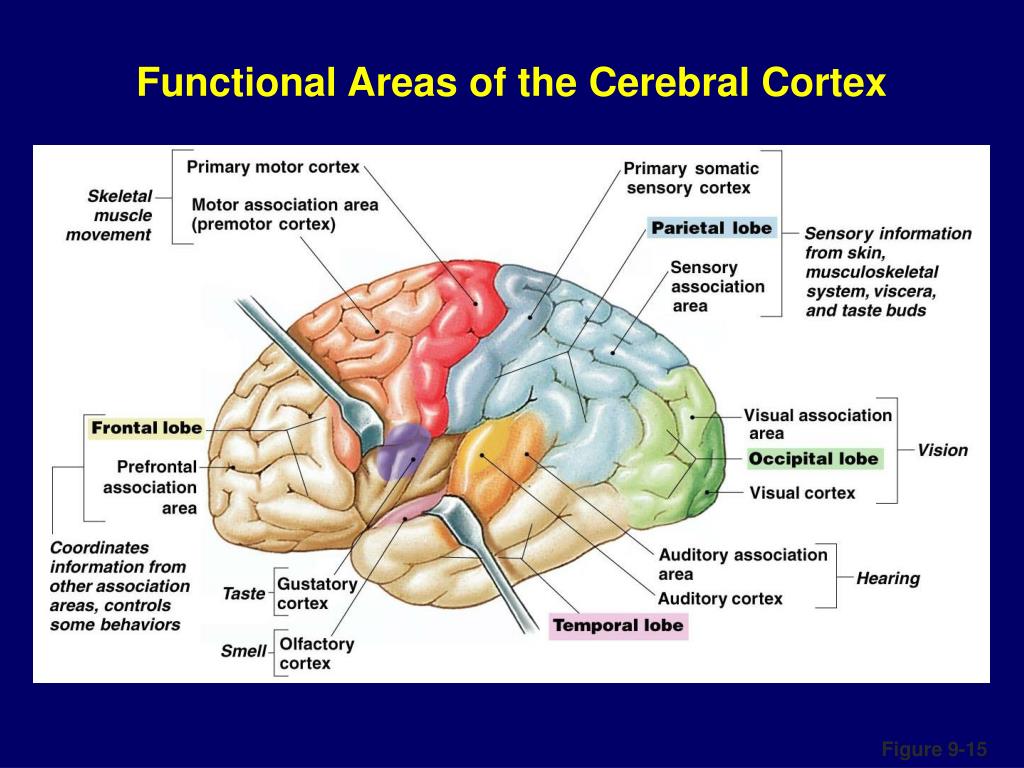
SOLUTION Lecture 20 functional anatomy of the cerebral cortex 1 Biology Diagrams The cerebral cortex (cortex of the brain) is the outer grey matter layer that completely covers the surface of the two cerebral hemispheres. It is about 2 to 4 mm thick and contains an aggregation of nerve cell bodies. This layer is thrown into complex folds, with elevations called gyri and grooves known as sulci.. The cerebral cortex is quite distinct from the cerebrum (forebrain) which The cerebral cortex is composed of a complex association of tightly packed neurons covering the outermost portion of the brain. It is the gray matter of the brain. Lying right under the meninges, the cerebral cortex divides into four lobes: frontal, temporal, parietal and occipital lobes, each with a multitude of functions. It is characteristically known for its bulges of brain tissue known as

The cerebrum consists of two cerebral hemispheres the outer layer called the cortex (gray matter) and the inner layer (white matter). There are four lobes in the cortex, the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, occipital lobe. This review article will focus on the functions of the cerebral cortex.

Neuroanatomy, Cerebral Cortex Biology Diagrams
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, [1] is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals.It is the largest site of neural integration in the central nervous system, [2] and plays a key role in attention, perception, awareness, thought, memory, language, and consciousness.The cerebral cortex is the part of the brain responsible for
The cerebral cortex carries out essential functions of your brain, like memory, thinking, learning, reasoning, problem-solving, emotions, consciousness, and sensory functions. What Is the Cerebral
Description, Anatomy, Function, & Disease - Britannica Biology Diagrams
But perhaps the most awe-inspiring function of the cerebral cortex is its role in higher-order cognitive functions. This is where things get really interesting. Problem-solving, abstract thinking, creativity - all these quintessentially human abilities emerge from the intricate dance of neurons in our cerebral cortex. It's the reason we can

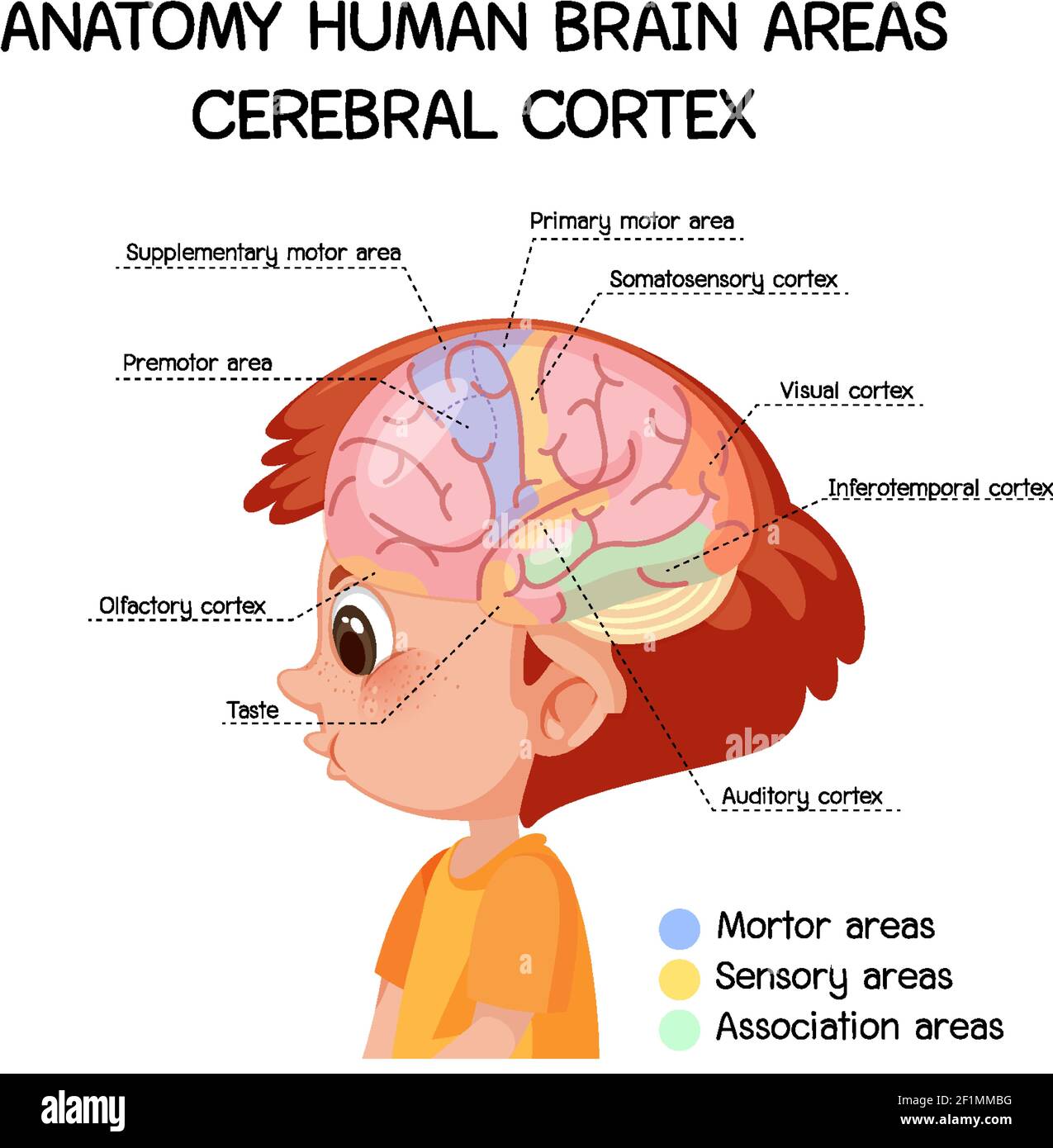
The cerebral cortex, a mere six millimeters thick, holds the key to our most complex thoughts, memories, and behaviors, making it the crown jewel of the human brain. This remarkable structure, often likened to a wrinkled, gray blanket draped over the brain's surface, is the epicenter of our cognitive abilities. The cerebral cortex is your brain's outermost layer. It's responsible for memory, thinking, learning, reasoning, problem-solving, emotions and functions related to your senses. Some researchers look at the brain in another way and classify the areas of the cerebral cortex by their three main types of functions: sensory, motor and
